9.3 A 40kHz-BW 90dB-SNDR Noise-Shaping SAR with 4× Passive Gain and 2nd-Order Mismatch Error Shaping
Abstract
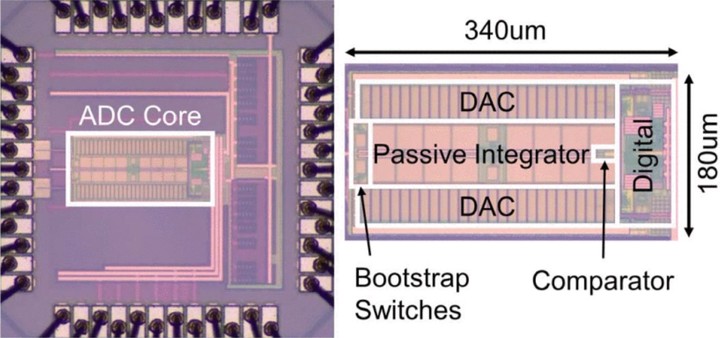
Noise-shaping (NS) SAR ADCs using passive loop filters have drawn increasing attention due to their simplicity, low power, zero static current, and PVT robustness. However, prior works show limited resolution (ENOB≤13b) due to two main challenges. The 1 st one is thermal noise. Passive loop filters cannot provide gain [1]. Hence, their suppression of the comparator noise is limited. In addition, every capacitor switching introduces extra kT/C noise. To reduce noise, a passive gain of 2 is realized in [2]. It also realizes passive voltage summation, which obviates the need for a multipath comparator, further reducing the comparator noise. Nevertheless, it uses small capacitors for residue sampling to minimize signal attenuation, leading to a large total kT/C noise of 20kT/C (C is the DAC size). Also, its NTF is mild (zero at 0.5), leading to limited SQNR benefit. The 2 nd challenge is DAC mismatch. Classic DEM is unsuitable for SARs with a high-resolution DAC due to excessive hardware cost. To reduce circuit complexity, Ref. [3] applies DEM only to the MSB part of the DAC, but the LSB part still produces considerable errors. The mismatch error shaping (MES) technique of [4] is well suited for high-resolution binary DACs due to low hardware complexity, but it has its own limitations. First, it can only achieve 1 st -order shaping with limited error suppression capability. Also, being 1 st -order, it has strong signal dependence and can produce considerable tones, especially at low input amplitudes. In addition, it suffers from signal range loss.